

HOME > About the center > Research buildings > Introduction of Research Laboratories of Material Cycles and Waste Management
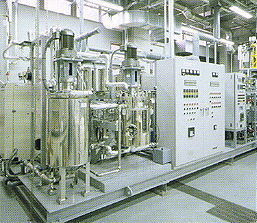
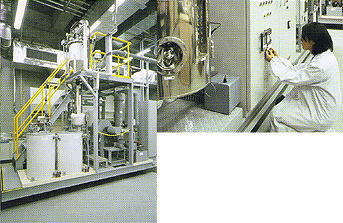
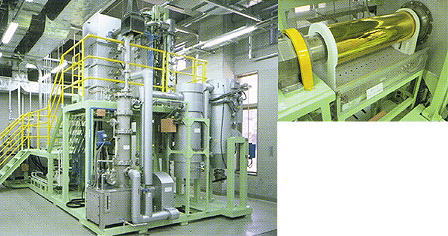
 This laboratory is used for clarifying the behavior of various substances in landfill conditions, assessing safety and stabilization,
and developing technologies and systems for landfills. It is equipped with landfill simulation lysimeters, which have an on-line monitoring
and automatic control system for temperature, moisture, and aerobic/anaerobic conditions to maintain environmental conditions close
to those in actual landfills. In addition, there are high-precision scales just under the landfill columns for monitoring the changes in weight,
thus permitting the precise calculation of mass balance. We are trying to clarify scientifically the changes and behaviors, such as leaching,
that landfill and micro-pollutants contained therein show over a long time by using these simulation plants.
This laboratory is used for clarifying the behavior of various substances in landfill conditions, assessing safety and stabilization,
and developing technologies and systems for landfills. It is equipped with landfill simulation lysimeters, which have an on-line monitoring
and automatic control system for temperature, moisture, and aerobic/anaerobic conditions to maintain environmental conditions close
to those in actual landfills. In addition, there are high-precision scales just under the landfill columns for monitoring the changes in weight,
thus permitting the precise calculation of mass balance. We are trying to clarify scientifically the changes and behaviors, such as leaching,
that landfill and micro-pollutants contained therein show over a long time by using these simulation plants.
 This room is designated for the preparation of samples by crushing and drying as a pretreatment for analysis of various types
of solid waste and recycling materials. It is equipped with powerful and versatile crushers which can cover from hard (e.g. melting slag)
to soft materials (e.g. waste plastics), and prepare samples having various particle sizes from rough to fine. Prepared samples are used
for various purposes such as a leachability test of hazardous substances and the investigation of pyrolysis characteristics. Installed in a space
completed with a vent duct for leak prevention and collection of odor are three large-sized dryers, which have sufficient capacity to dry a
large amount of wet waste in a short time. They are used for pre-treating samples for garbage composition analysis, three-component
analysis (combustibles, ashes, water), heat value analysis and elemental composition analysis performed in a dried state.
This room is designated for the preparation of samples by crushing and drying as a pretreatment for analysis of various types
of solid waste and recycling materials. It is equipped with powerful and versatile crushers which can cover from hard (e.g. melting slag)
to soft materials (e.g. waste plastics), and prepare samples having various particle sizes from rough to fine. Prepared samples are used
for various purposes such as a leachability test of hazardous substances and the investigation of pyrolysis characteristics. Installed in a space
completed with a vent duct for leak prevention and collection of odor are three large-sized dryers, which have sufficient capacity to dry a
large amount of wet waste in a short time. They are used for pre-treating samples for garbage composition analysis, three-component
analysis (combustibles, ashes, water), heat value analysis and elemental composition analysis performed in a dried state.




 Continual comprehensive monitoring of various hazardous substances that may be included in waste or produced during waste-recycling
and treatment is difficult with conventional chemical analysis only. The bioassay (or biotest), which uses cultured cells, microbes,
fish or other organisms, is designed to obtain quick and comprehensive information on the harmful effects of chemical substances
on living organisms, and so has been used as complementary method for whole hazard monitoring and assessment. This laboratory
is equipped with constant-temperature aquariums for breeding and keeping aquatic organisms for tests, an isolated clean room for
safely testing microbes, and micro-plate readers for detecting absorption, fl uorescence and bioluminescence for simultaneously treating
many samples. Using these instruments, we are developing reasonable sets of bioassay methods (i.e. "batteries") employing a range
of living organisms from microorganisms to higher animals such as frogs and fish for the examination of waste and recycling resources.
The batteries are also useful for monitoring the effects of chemicals in emissions from waste treatment, recycling and disposal facilities.
Continual comprehensive monitoring of various hazardous substances that may be included in waste or produced during waste-recycling
and treatment is difficult with conventional chemical analysis only. The bioassay (or biotest), which uses cultured cells, microbes,
fish or other organisms, is designed to obtain quick and comprehensive information on the harmful effects of chemical substances
on living organisms, and so has been used as complementary method for whole hazard monitoring and assessment. This laboratory
is equipped with constant-temperature aquariums for breeding and keeping aquatic organisms for tests, an isolated clean room for
safely testing microbes, and micro-plate readers for detecting absorption, fl uorescence and bioluminescence for simultaneously treating
many samples. Using these instruments, we are developing reasonable sets of bioassay methods (i.e. "batteries") employing a range
of living organisms from microorganisms to higher animals such as frogs and fish for the examination of waste and recycling resources.
The batteries are also useful for monitoring the effects of chemicals in emissions from waste treatment, recycling and disposal facilities.
 "Information" is playing an increasingly important role today. We are trying to improve the collection, storage, and dissemination of
accurate information and analysis to support the establishment of a sound materialcycle society. This room is equipped with
computers for analysis, a server for distributing information, a large plasma display, and others. These are used for our studies on: the analysis
of material flows of resources, products and waste; the development of the LCA (life cycle assessment) method; support for the
proper management of recyclable resources and waste with information technologies such as GIS (geographic information system)
and remote sensing; and the establishment of an effective recycling system tailored to regional characteristics. These are also used
for providing information on our activities including our research results.
"Information" is playing an increasingly important role today. We are trying to improve the collection, storage, and dissemination of
accurate information and analysis to support the establishment of a sound materialcycle society. This room is equipped with
computers for analysis, a server for distributing information, a large plasma display, and others. These are used for our studies on: the analysis
of material flows of resources, products and waste; the development of the LCA (life cycle assessment) method; support for the
proper management of recyclable resources and waste with information technologies such as GIS (geographic information system)
and remote sensing; and the establishment of an effective recycling system tailored to regional characteristics. These are also used
for providing information on our activities including our research results.